Science
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE: beginning of a new era of technology
People have been synthesizing automatons for a long time, but artificial intelligence was first discussed in the 1950s, after Herbert Simon argued that computers could think, based on the ideas of Alan Turing. Subsequently, artificial intelligence became established. The technologies that assist in the handling of knowledge are broadly referred to as artificial intelligence (AI). A broad overview of artificial intelligence and a more detailed view of its two branches – expert systems and neural networks – are given in this chapter.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is concerned with using computers to perform tasks that would be called ‘intelligent’ if people did them. The objectives are two-fold: to improve understanding of human cognition and to improve the potential of the computer as a tool for problem-solving.
According to Holsapple and Whinston (1987), ‘artificial intelligence is the activity of providing such machines as computers with the ability to display behavior that would be regarded as intelligent if it were observed in humans.’
Another definition of artificial intelligence is: ‘A field of study that designs and develops machines capable of performing tasks that would require intelligence if performed by a human being (Rich, 1987).
HISTORY OF AI
The term AI was coined by Jhon McCarthy as the theme of a conference held at Dartmouth College. In the same year, the first AI computer program, called Logic Theorist, was announced. This program encouraged researchers to develop another program, called the General Problem Solver (GPS), that was intended for use in solving problems of all kinds.
For the past 15-20 years, there has been an increasing interest in using the computer for artificial intelligence. The idea is to develop a machine that can reason, learn, understand, recall and explain its behavior, and actions can be viewed as an intelligent machine. However, even today, three to four decades after AI was conceived, the creation of truly intelligent machines is still not quite a reality.
AREAS OF AI
The areas that influence AI and the branches of AI are expert systems, robotics, natural language, learning, computer vision, perceptive systems, AI hardware, and neural networks. These areas are illustrated in the below figure which indicates a certain amount of overlap among the areas. The overlap illustrates the way that one area can benefit others. A brief explanation of various branches of AI is given.
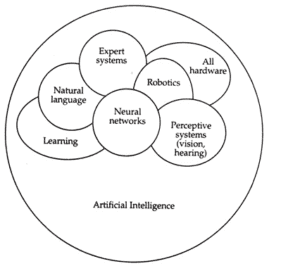
- Expert systems are computer programs that attempt to represent the knowledge of human experts, in the form of heuristics, in a specialized area. An expert system stores the knowledge of an expert in a specific area of studies, such as production engineering and genetic engineering. The system applies various reasoning methods to the information stored in it, in order to solve complex problems that require both knowledge and intuition. Sometimes, the problem-solving capabilities of such systems are as good as, or even better than, those of human experts.
- Perceptive systems use visual images and auditory signals to instruct computers or rather devices, such as robots.
- Computer vision is to endow computers with the ability to recognize and identify objects and the context to which they belong. Vision capabilities enhance the ability of computers to emulate human intelligence.
- Natural language processing enables users to communicate with the computer in foreign languages.
- Learning encompasses all of the activity that enables the computer to or another device to acquire knowledge in addition to what has been entered into the memory by its manufacturer or by programmers.
- AI hardware includes the physical device that aid in AI application.
- Robotics consists of computer-controlled devices that mimic the motor activities of humans.
- Neural networks are highly simplified models of the human nervous system that exhibit abilities such as learning, generalization, and abstraction. These abilities enable the models to learn human-like behavior.
Usage of AI
AI is important because it can help solve immensely difficult issues in various industries, such as entertainment, education, health, commerce, transport, and utilities. AI applications can be grouped into five categories:
- Reasoning: The ability to solve problems through logical deduction. e.g. financial asset management, legal assessment, financial application processing, autonomous weapons systems, games
- Knowledge: The ability to present knowledge about the world. e.g. financial market trading, purchase prediction, fraud prevention, drug creation, medical diagnosis, the media recommendation
- Planning: The ability to set and achieve goals. e.g. inventory management, demand forecasting, predictive maintenance, physical and digital network optimization, navigation, scheduling, logistics
- Communication: The ability to understand spoken and written the language. e.g. real-time translation of spoken and written languages, real-time transcription, intelligent assistants, voice control
- Perception: The ability to infer things about the world via sounds, images, and other sensory inputs. e.g. medical diagnosis, autonomous vehicles, surveillance.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has often been popularly envisaged in super-smart humanoid robot form. In fact, it’s more commonly implemented as behind-the-scenes algorithms that can process ‘big’ data to accomplish a range of relatively mundane tasks far more efficiently than humans can.
Prospects of AI
In the next 10 years, technologies in narrow fields such as speech recognition will continue to improve and will reach human levels. In 10 years AI will be able to communicate with humans in unstructured English using text or voice, navigate (not perfectly) in an unprepared environment and will have some rudimentary common sense (and domain-specific intelligence).
It will recreate some parts of the human (animal) brain in silicon. The feasibility of this is demonstrated by tentative hippocampus experiments in rats. There are two major projects aiming for human brain simulation, CCortex, and IBM Blue Brain.
There will be an increasing number of practical applications based on digitally recreated aspects of human intelligence, such as cognition, perception, rehearsal learning, or learning by repetitive practice. Robots take over everyone’s jobs.
The development of meaningful artificial intelligence will require that machines acquire some variant of human consciousness. Systems that do not possess self-awareness and sentience will at best always be very brittle. Without these uniquely human characteristics, truely useful and powerful assistants will remain a goal to achieve.
Challenges of AI
The foremost factor is blockchain technology (also known as Distributed Ledger Technology) and its potential seismic impact on financial transactions across the globe. Blockchain technology has started sweeping the different areas of transactional finance, such as clearing, settlement, payments. Secondly, although it is still in its infancy, we know that there are many algorithmic trading systems used around the world in different streams of asset management.
Challenges and cope up in Indian context
Indians must upskill in the IT sector to survive and this is increasingly acknowledged. But there are constraints that go beyond an over-emphasis on low-end technical services. While the country is not an entrepreneurial epicenter for artificial intelligence, many of the executives who are a part of the ecosystem of over 170 AI startups point out that they face enormous staffing challenges.
There simply is not enough AI talent in the country as only 4% of AI professionals in India have worked on emerging technologies such as deep learning and neural networks and many companies require candidates to have a Ph.D. in the field, which is even scarcer in India.
According to AI startup founders Subrat Parida and Navneet Gupta, they spend 40% of their time just looking for talented engineers and it is immensely difficult to find people with the right training and experience in AI.
India must address its shortage of engineers with training in machine learning, analytics, and robotics. However, the problems go beyond training. There is a particular mindset that is required as AI is a discovery-oriented and novel field that requires professionals with an appetite for research and experimentation.
Thus, the challenges experienced by Indian startups in AI are related to a deeper problem. But the threat posed by automation and artificial intelligence means that the greatest risk of all is not acting, not investing and not innovating in the technologies of the future.
Although we don’t know the exact future, it is quite evident that interacting with AI will soon become an everyday activity. These interactions will clearly help our society evolve, particularly in regards to automated transportation, cyborgs, handling dangerous duties, solving climate change, friendships and improving the care of our elders. Beyond these six impacts, there are even more ways that AI technology can influence our future and this very fact has professionals across multiple industries extremely excited for the ever-burgeoning future of artificial intelligence.






































Sanjay Kumar pal
July 29, 2019 at 11:18 AM
AI is the new age technology which will make way for easy living …
Bishnu pada Choudhury
July 30, 2019 at 1:09 AM
Good information about AI portrayed by author sp pattanaik. It is the latest invention of modern era.
Sarada
July 30, 2019 at 2:45 AM
Thanks for ure valuable suggestion
Sarada
July 30, 2019 at 2:45 AM
Thanks for ure valuable information