Science
Humanoid Robots Part 1: The Journey

We have already talked about Artificial intelligence and how far it has come in two of our previous articles. Now it’s time to talk about the biggest example of the advancement of Artificial Intelligence- humanoid robots.

Robots come in all shapes and sizes but the ones that built to resemble a human body are known as Humanoid Robots. Some of them have complete parts like a head, torso, legs and arms while some may only be built to resemble some specific parts. In any case, they are a huge help while researching different aspects of being human like bipedal locomotion or interaction with the surrounding and even consciousness.
Let’s take a look at their journey, from where they began and how far they have come –
ANCIENT TIMES TILL 19TH CENTURY
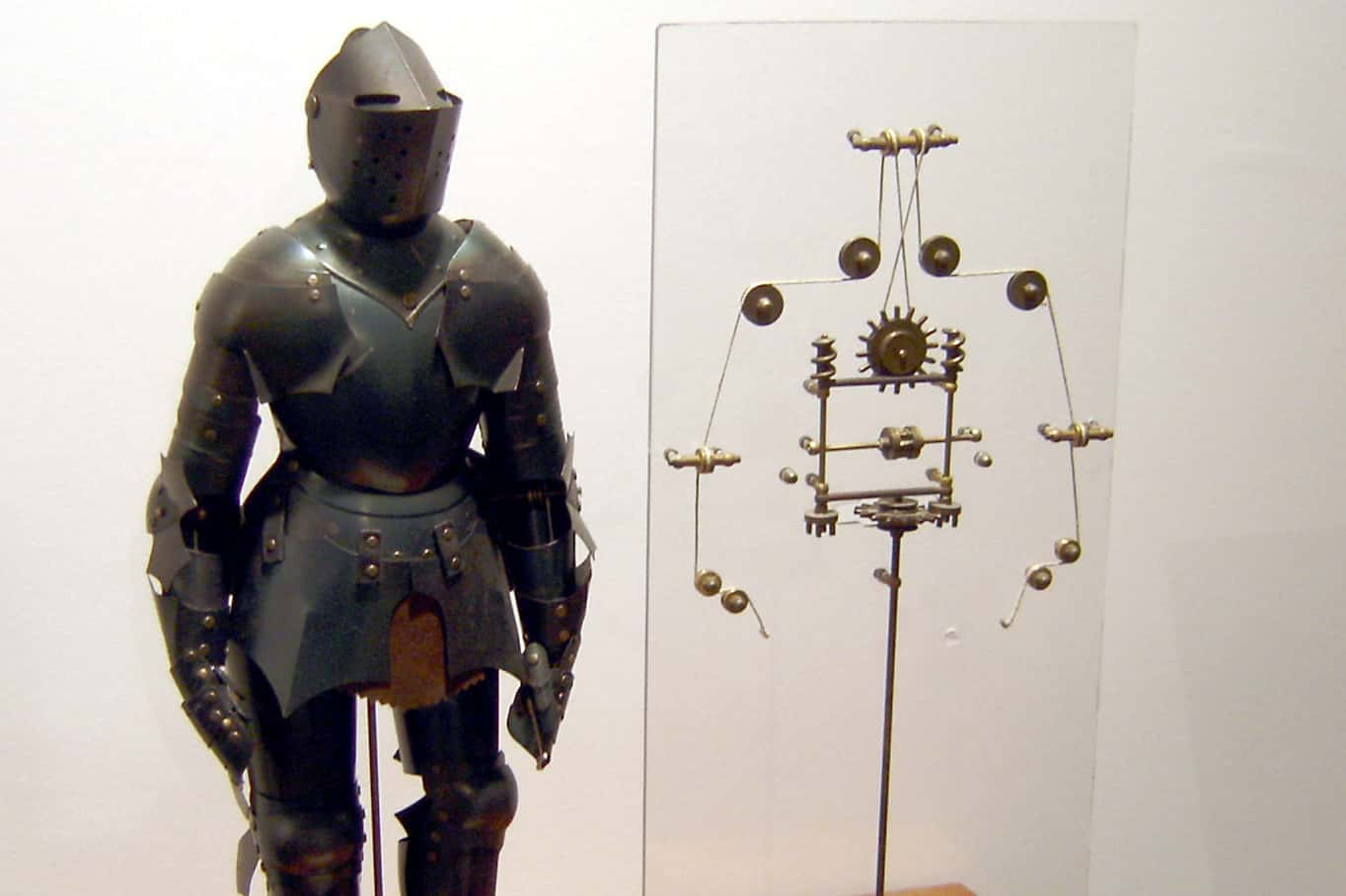
As with A.I. the humanoid robots too find mention in a number of antiquarian works specially Greek. Even as early as the 13th century, Al-Jazari, a Turkish Polymath described quite a number of humanoid automata ranging from a band to humanoid servants. And how can we forget Leonardo da Vinci who by the end of the 15th century had already designed Leonardo’s Robot- a humanoid automation that looks like an armored knight.
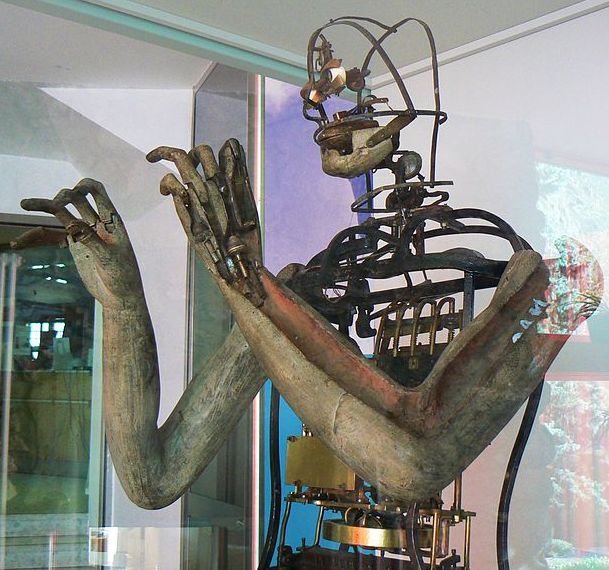
Of course real development began in 18th century when in 1738, Jaques de Vaucanson built the ‘Flute Player’ and the ‘Tambourine Player’ who could play a dozen of different songs on the instruments. Also in 1774 Pierre Jacquet-Droz along with his son created the Draughtsman, the Musicienne and the Writer, resembling a boy that could write messages up to forty characters long.
If you have seen the 2011 movie Hugo, you would have a faint idea of what kind of devices we are taking about but don’t worry if you don’t, here are some pictures –



Moving on, in the 19th century we have Nikola Tesla, one of the greatest inventors of all time and it was in 1898 that he publicly demonstrated his automaton technology. At the Electrical Exposition held at New York, he controlled a model boat,which was wireless. Of course though it wasn’t humanoid, it was still a major development which gave way to more humanoid automatons. And thus ended the 19th century.
THE 20TH CENTURY
The 20th century in itself was legendary given how many inventions it gave us and how many cutting edge technologies are rooted in this time period. It was the same for Humanoid Robots as the 20th century brought some major developments in the field and the first proper humanoid robots themselves.
In 1928, Eric the electrical robot was opened for exhibition in London. The years before this one saw ‘Robots’, the term being coined in a 1921 play, a part of a number of movies and popular media, pointing to their widespread popularity. In the early 1940’s, Isaac Asimov who gave us a number of sci-fi stories featuring Robot, coined the term ‘Robotics’ and formulated the Three Laws of Robotics.
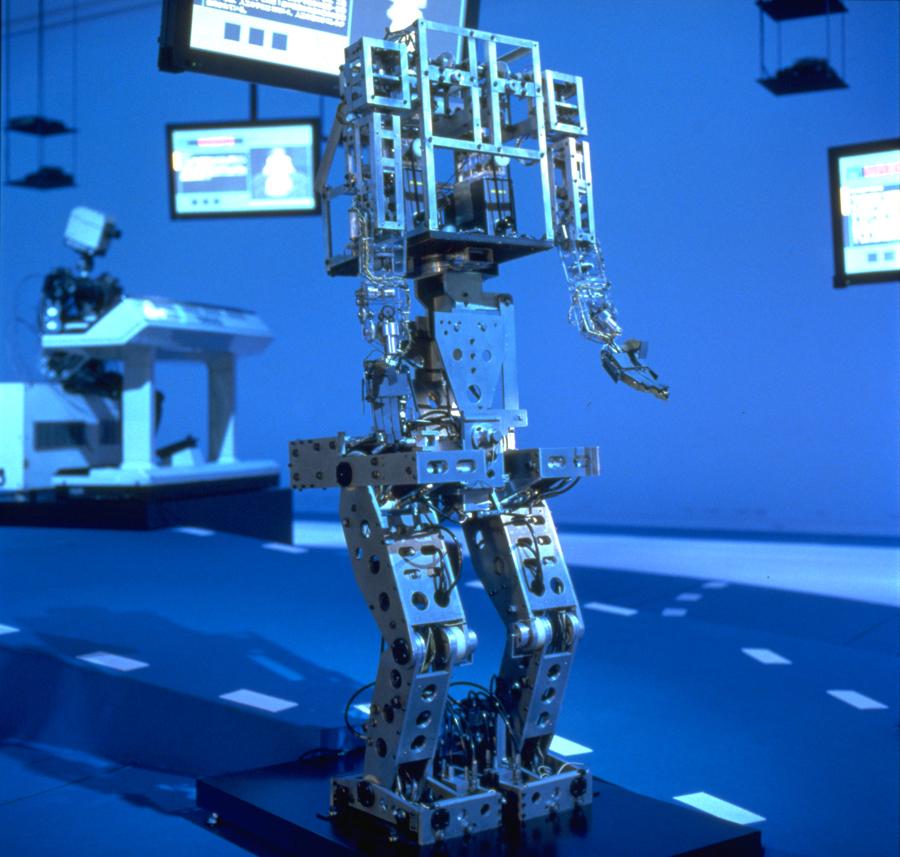
WABOT-1
In 1948, Norbert Wiener gave us the principles of Cybernetics, which became the basis of practical robots and in 1972 we got WABOT-1, world’s first full-scale humanoid intelligent robot. WABOT-1 was the first android able to walk, communicate with a person, measure distances and direction to the objects and even grip and transport objects with hands. It was a part of the WABOT Project started in 1967 by the Waseda University in Japan.
Things really got interested for the research relating to robots around this time as a number of scientific papers and theories were published resolving a number of issues and furthering the development of Humanoid Robots, especially Miomir Vukobratovic’s ‘Zero Moment Point’, a theoretical model to explain biped locomotion. He also had a hand in building the first active anthropomorphic exoskeleton in 1972.

The 1980s were on a completely different level as they gave us Greenman (1983), WABOT -2 (1984), Hitachi’s biped WHL-11 (1985), another musician robot WASUBOT from Waseda University (1985) and Honda’s biped robot E0 which was followed by six others (E1 to E6) in the subsequent years. Also, before the decade ended, in 1989, we also got Manny, a full scale anthropomorphic robot which could walk, crawl and even had an artificial respiratory system.
1990s TO 2013
We are lumping the last decade of 20th century and the 21st century together as things developed one after the other starting from 1993 when Honda developed P1 (Prototype Model 1) through P3, an evolution of its E series.
In 1995, Waseda University furthered its research and came up with Hadaly and Wabian. 1996 saw Saika, a human-size, light weight humanoid robot from Tokyo university. Hadaly 2 was developed in 1997 and it could interactively communicate with humans.

The start of 21st century saw Honda’s ASIMO, the biped which could run and walk like humans. In 2001 we have Sony Dream Robot (SDR, later renamed Qrio) and Fujitsu’s first commercial robot HOAP-1. Another autonomous biped robot JOHNNIE was developed at the Technical University of Munich in 2003. Actroid, a robot with realistic silicone skin was developed by Osaka University in the same year.
The next decade, 2004 to 2013 was likewise filled with dozens of Humanoid robots being developed and unveiled one after the other all over the world. These robots include Persia (Iran’s first humanoid robot in 2004); KHR-1, Wakamaru and the Geminoid series from Japan; Nao in France, RoboTurk sponsored by the Turkish Government; REEM-A (first fully autonomous European biped humanoid robot in 2006) and Mahru from South Korea along with Germany’s TORO.

NEXI
This time-period also gave us Nexi, the first mobile and social robot; Salvius, the first open-source humanoid robot from US; Kobian from Waseda University that can walk, talk and mimic emotions; Robonaut-2 from NASA; singing and dancing robot HRP-4C from Japan; Honda ASIMO’s second generation and Poppy, the first open source 3D-printed humanoid robot.
2014 onwards were even bigger in terms of achievements and cutting edge technology. The past 5 years gave an entirely new face to the humanoid robots but we’ll leave it for another day… or rather another article!