Of Law & Legal
What Is External Commercial Borrowing (ECB) – Who Can Raise Till What Limit?
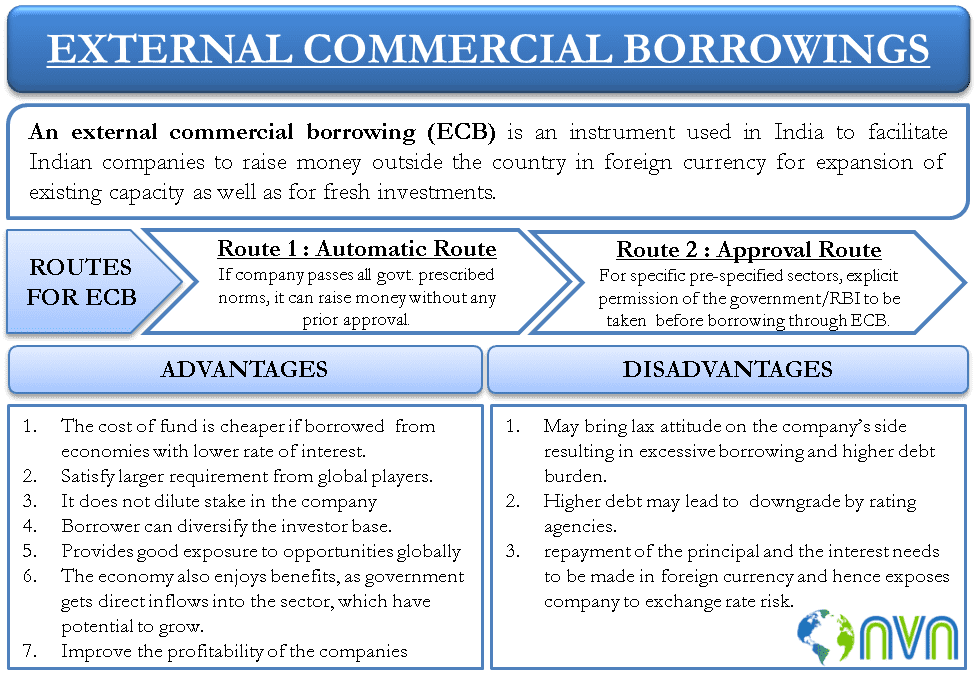
External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs) occupy a very important position as a source of funds for Corporate. The main purpose of ECB is to encourage borrowings which provides the basis for the strongest economy. Thus, ECB is not only a three-letter word but a lifeline of the corporate world.
External Commercial Borrowing (ECB), as the expression hints, contains livelihood to some extent to persons in the corporate world. It is the loan/debt/borrowings taken by an eligible entity in India for commercial purposes, externally i.e. from any recognized entity outside India. However, these borrowings taken must conform to the norms of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
The ECB’s are governed by the regulations of RBI under Master Direction – External Commercial Borrowings, Trade Credits and Structured Obligations (Master Direction), and Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA).
All infrastructure and Greenfield projects can raise up to 50% of the total project cost while Telecom Projects up to 50% of the project cost (including license fees). In the case of power projects, greater flexibility will be allowed based on merits. The Master Direction has also clearly mentioned the negative list for which ECBs cannot be used are as below:
- Real estate activities.
- Investment in the capital market.
- Equity investment.
- On-lending to entities for the above activities, except in case of ECB raised by NBFCs as given under the Master Direction.